Introduction
Brief explanation of carbide inserts and their significance in machining.
Importance of identifying carbide inserts correctly for optimal performance.

Understanding Carbide Inserts
Definition and composition of carbide inserts.
Explanation of how carbide inserts are different from other cutting tool materials.
Carbide inserts are essential components in modern machining processes, known for their exceptional durability and precision. These inserts are predominantly composed of tungsten carbide, a composite material formed by combining tungsten (a heavy, dense metal) with carbon. The resulting tungsten carbide is extremely hard and wear-resistant, making it ideal for cutting and shaping various materials. This composite is often combined with a binder material, such as cobalt, which enhances toughness and helps hold the tungsten carbide grains together.
What sets carbide inserts apart from other cutting tool materials, such as high-speed steel (HSS) or ceramics, is their remarkable hardness and resistance to heat and wear. While HSS tools may exhibit good cutting performance, carbide inserts excel in demanding applications where high cutting speeds, heavy loads, and abrasive materials are encountered. The hardness of carbide ensures prolonged tool life and minimal edge deformation, contributing to consistent and precise machining results. Moreover, carbide inserts have the advantage of retaining their cutting edge at elevated temperatures, making them well-suited for high-speed and high-temperature cutting operations.
In contrast, ceramics are prized for their high-temperature stability and chemical resistance, but they can be brittle and prone to chipping under certain conditions. Carbide inserts strike a balance between hardness, toughness, and thermal resistance, making them a preferred choice for a wide range of machining tasks. Their versatility, combined with their ability to maintain sharp cutting edges and endure challenging machining environments, positions carbide inserts as indispensable tools in modern manufacturing processes.
Physical Characteristics of Carbide Inserts
Overview of the common shapes and sizes of carbide inserts (e.g., square, triangular, round).
Discussion on the color-coding system for insert identification.
Explanation of the various chip breaker designs and their purposes.
Carbide inserts boast a diverse range of physical characteristics that are finely tuned to optimize machining performance. Firstly, these inserts come in a variety of shapes and sizes tailored to specific cutting tasks. Common shapes include square, triangular, round, and parallelogram, each designed to address different machining requirements and geometries. Triangular inserts, for instance, are ideal for general turning operations, while square inserts excel in facing and shoulder milling. Round inserts are often used for profiling and contouring, showcasing the adaptability of carbide inserts to various machining scenarios.
In addition to shapes and sizes, a color-coding system is often employed for insert identification. Different manufacturers may use distinct color schemes to indicate insert types, grades, and intended applications. This system streamlines the selection process and helps machinists quickly identify the most suitable insert for a specific machining task, enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy.
Another critical aspect is the design of chip breakers on carbide inserts. Chip breakers are strategically engineered features along the cutting edge that help control chip formation and evacuation during machining. These designs play a vital role in preventing chip entanglement, reducing heat generation, and enhancing chip disposal. Chip breakers vary in shape and placement, with options like straight, curved, and wavy configurations. The choice of chip breaker design depends on factors such as material type, cutting depth, and feed rate. For instance, a deep and robust chip breaker may be utilized for heavy roughing, while a finer chip breaker is preferred for finishing operations. The careful selection of chip breakers ensures improved chip control, reduced tool wear, and enhanced surface finish, highlighting the precision engineering inherent in carbide insert design.
Carbide inserts’ physical characteristics encompass a spectrum of shapes, sizes, color codes, and chip breaker designs. These aspects collectively empower machinists with the versatility and precision needed to achieve optimal results across a wide range of machining applications.
Identification Methods
Visual inspection: Detailed steps for visually identifying carbide inserts based on shape, color, and markings.
Measurements: How to use calipers or micrometers to measure insert dimensions accurately.
Magnetism test: How to perform a magnetism test to differentiate between carbide and other materials.
There are several reliable methods for effectively identifying carbide inserts, ensuring accurate selection and optimal performance.
Visual Inspection: Visual inspection involves a comprehensive assessment of the insert’s physical attributes. Begin by examining the insert’s shape, as carbide inserts come in various geometries like square, triangular, or round. Compare the insert’s form with known carbide insert shapes to determine compatibility. Additionally, pay attention to color-coded markings that often indicate specific insert types or grades. These markings can provide valuable insights into the insert’s intended use. Detailed examination of the insert’s surface can also reveal any unique features or symbols that further aid in identification.
Measurements: Precise measurements are crucial in distinguishing carbide inserts accurately. Utilize calipers or micrometers to measure key dimensions such as the insert’s length, width, and thickness. Compare these measurements to standard specifications provided by manufacturers or industry guidelines. Carbide inserts often have specific dimensions that differentiate them from other materials. Careful measurement ensures that the insert’s size aligns with the intended application.
Magnetism Test: Conducting a magnetism test is another effective method for differentiating carbide inserts. Tungsten carbide, the primary component of carbide inserts, is not magnetic. To perform the test, bring a magnet close to the insert’s surface. If the insert is attracted to the magnet, it likely contains a significant amount of steel and is not a pure carbide insert. Conversely, if the insert exhibits little to no attraction, it is likely composed of carbide material.
By employing these identification techniques—visual inspection, measurements, and a magnetism test—machinists can confidently and accurately differentiate carbide inserts from other materials. This proficiency in identification ensures that the right insert is selected for the intended application, contributing to efficient and successful machining outcomes.
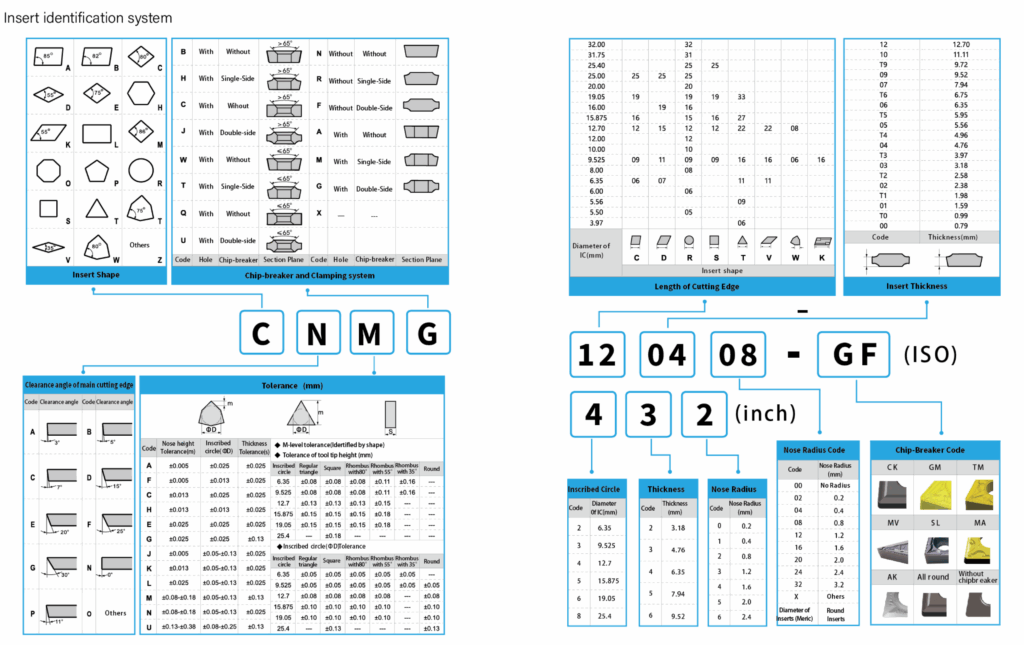
Understanding Insert Markings
Interpretation of markings, codes, and symbols found on carbide inserts.
Explanation of ISO and ANSI insert designation systems.
Carbide inserts are often adorned with markings, codes, and symbols that convey essential information about their specifications and intended uses. Understanding these markings is crucial for selecting and utilizing carbide inserts effectively. Firstly, these markings typically include alphanumeric codes that denote key characteristics such as insert type, geometry, and cutting parameters. Deciphering these codes allows machinists to quickly identify the insert’s application range and compatibility.
Moreover, symbols may be engraved on carbide inserts to provide additional insights into their capabilities. Symbols indicating chip breaker design, recommended cutting direction, and tolerance levels can help machinists make informed decisions when choosing inserts for specific machining operations.
To bring further clarity, carbide inserts adhere to international standards for designation, with two prominent systems being ISO (International Organization for Standardization) and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). The ISO system employs a standardized alphanumeric code that encapsulates insert geometry, cutting edge properties, and cutting direction. This comprehensive code aids in universal insert identification across different manufacturers and regions.
On the other hand, the ANSI insert designation system, commonly used in North America, focuses on a numerical code for insert shape and size. While less detailed than the ISO system, the ANSI system is straightforward and easily understood, simplifying insert selection for those familiar with its conventions.
Understanding these markings and designation systems empowers machinists to make informed decisions when selecting carbide inserts, ensuring compatibility with their machining tasks and materials. This knowledge enhances operational efficiency and precision, underscoring the importance of accurate interpretation in optimizing machining outcomes.
Common Applications of Carbide Inserts
Overview of industries and materials where carbide inserts are commonly used.
Brief discussion on selecting the right insert type for specific applications.
Maintenance and Care
Tips for extending the lifespan of carbide inserts.
Proper storage practices to prevent damage or contamination.
Conclusion
Recap of key points for identifying carbide inserts accurately.
Emphasis on the importance of proper identification for efficient machining operations.
Reasoning for the Outline:
This outline provides a comprehensive guide to identifying carbide inserts, catering to readers with varying levels of familiarity with the subject. By including detailed steps for visual identification, measurements, and magnetism tests, readers can confidently determine whether an insert is made of carbide. The outline also addresses the importance of insert markings and their interpretation, which is crucial for proper usage.
Additionally, discussing common applications and maintenance tips enhances the article’s value, offering readers practical insights into maximizing the utility and lifespan of carbide inserts. The outline follows a logical flow, starting with foundational knowledge and gradually delving into more specific details. This structure ensures that readers can easily follow along and grasp the information presented.
